What Is a Porous Fiber Matrix?
A fiber matrix is a material made up of bonded fibrous strands that form two-dimensional cross-sections. These cross-sections can be extruded into versatile three-dimensional shapes. What makes it unique is the presence of voids or pores that are strategically positioned between the fibrous strands. These pores are essential in managing fluids, allowing for rapid flow or enhanced liquid absorption.
The manufacturing process of fiber matrix involves the application of heat and pressure, similar to the process used for sintered materials. However, instead of bonding particles, the process bonds fibrous strands. Customized fibers are wrapped in an outer sheath, and these fibers are bonded in various configurations. This innovative process doesn’t rely on traditional knitting or weaving but instead focuses on forming fibrous components, such as sheets, rods, tubes, blocks, and 3D geometries.
Fiber Matrix Material Options
Several polymers prove suitable for fiber matrix, each possessing distinct properties tailored to specific applications. Consider some of the primary material options:
Polyolefins such as LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE, and PP are widely used materials due to their simple molecular structure. However, it’s important to keep in mind that they may have temperature limitations depending on the application. Polyesters, including PET, PTT, and PBT, are very versatile and compatible with almost all fiber technology platforms, making them a reliable choice for various situations. Polyamides like Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6 are the preferred choices for applications that require heat resistance and chemical compatibility. They are widely used in applications that range from hygroscopic to hydrophilic.

Talk with a Material Science Expert
Additionally, there are other suitable materials to consider based on your specific requirements. For biodegradable applications, cellulose acetate (CA) is a sustainable choice. Polylactic acid (PLA) serves as a renewable raw material, while polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) excels in high-temperature resistance applications. Furthermore, numerous co-polymers offer diverse configurations, adding to the array of options available. Collaborating with an application engineer is vital to selecting the right materials for your needs.
Key Properties
Fiber matrix has several key properties that make it a versatile and effective material for various applications. Its controlled pore size and pore volume are some of its most defining features, allowing for finely tuned pathways for precise control over wicking speed, wicking distance, and filtration efficiency. Furthermore, the density of the fiber matrix can be optimized for speed and overall flow. Lastly, it’s essential to consider the chemicals they will come into contact with. Below, you can find a table showing the chemical compatibility of common polymers.
| Chemicals | PE, PP | PET, PEB | N6, N6,6 | CA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acids (non oxidizing) | Good | Good | Poor | Poor |
| Bases | Good | Poor | Good | Poor |
| Oil | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| Aromatic solvents | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| Non-polar aliphatic solvent | Fair | Good | Good | Good |
| Polar-aprotic solvents | Fair | Good | Fair | Fair |
| Polar-Protic solvents | Fair-Good | Fair-Good | Good | Good |
| Halogenated solvent | Good | Good | Good | Poor |
| Oxidizing agents | Poor | Poor | Good | Good |
Fiber Matrix Applications
At Porex, our collaborative engineering approach cultivates innovative solutions for both novel and established products. We address functional design complexities in wicking, filtration, diffusion, and application by leveraging our comprehensive expertise in porous material science, product design, and custom plastic manufacturing.
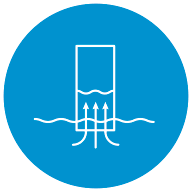
Wick
A fiber matrix’s capillary structure excels in fluid transfer applications, such as point-of-care diagnostic sample testing, dialysis treatments, and commercial applications, such as inkjet printing cartridges.
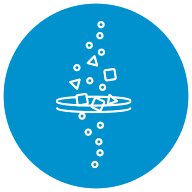
Filter
Porous fibers are useful in separating solids or liquids from a mixture. They have a variety of applications, including automotive oil and fuel water separation filters, glass shard filters for life science applications, and liquid contaminant removal filters for both consumer and industrial segments.

Diffuse
Precision control over diffusion rates is key in various applications, from bioprocessing spargers to plug-in air fresheners.

Apply
Application products such as whiteboard marketers work great with porous fiber nibs. The material allows the ink to be applied evenly and completely onto a surface or substrate.
Explore Solutions for Your Product
If your product involves fluid management, Porex’s solutions can provide significant benefits. If you’re considering a finer matrix, our material science experts are ready to assist. Reach out to ASK AN ENGINEER or REQUEST A SAMPLE, ensuring a customized solution for your unique requirements.
