What is Porous Plastic?
Absorb | Apply | Articles | Diffuse | Filter | Membranes | Porous Fiber | Porous Foam | Sintered Porous Plastic | Sustainable | Vent | Wick |
Is plastic porous? Yes, but how porous plastic is created requires precise manufacturing techniques. You may have heard the term porous plastic but aren’t quite sure what it means. The term is fairly common among engineers and R&D teams as they source materials to build products. But what exactly is porous plastic? We’ll explore what this material is and what it can do.
How Is Plastic Porous?
The simplest definition of porous plastic is a breathable, versatile material that’s used in a lot of different products. The complex definition is a bit more scientific.
Manufacturing a Porous Medium
What makes plastic porous has to do with how it’s made. Using controlled heat and pressure, engineers fuse particles together to create a connected pore structure that can be tailored to control the flow of particles within the device — including gases, liquids, light, and sound. This differs from injection molding, which liquefies the materials.
It’s probably best understood by looking at a few examples. Foam applicators used to apply makeup are made of porous plastic, as are the wicks inside plug-in air fresheners and the nib on your highlighter used to apply the ink. In both cases, the end product requires a high level of control over the flow of gas and liquids inside it.
With the makeup applicator, the material has to wick yet absorb enough makeup for application. With the air freshener, the wick slowly diffuses the liquid fragrance into the air. Both products require a component that helps control the flow of gases and liquids.
What Types of Plastics Are Porous?
There are four main types of plastic that are used to create a porous medium: sintered plastics, fiber, foam, and membranes. Sintered porous plastics involve fusing polymers or particles to create a porous medium and establish controlled pore sizes, yielding a robust, self-supporting material. Porous fibers are the result of bonded fibers, producing materials with adaptable fluid transfer capabilities ideal for medical, industrial, and consumer applications. Porous foam is a specialized amalgamation of materials with diverse pore sizes, densities, and softness, notably valued for its fluid absorption proficiency in medical-grade and cosmetic applications.
Lastly, porous membranes hold a crucial role in precision-driven processes. These membranes offer consistent and reproducible pore structures, utilizing a range of materials, including PTFE, Oxyphen track-etched, and PES membranes.
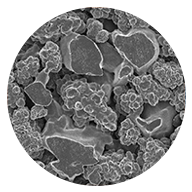
Sintered Porous Plastics
Engineered from various polymers with controlled pore sizes to provide outstanding strength, durability, chemical resistance, resiliency, and design flexibility across multiple applications.
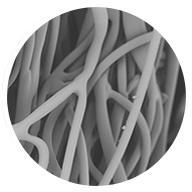
Porous Fiber
Fibers are bonded together to create two-dimensional cross-sections and extruded to create three-dimensional shapes. A blend of polymeric fibers bonded together for ideal fluid handling capillary structures.
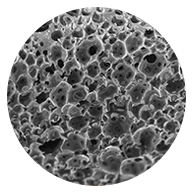
Porous Foam
A two-step pre-polymer process that uses customized blends of raw materials through a clean polyurethane process without the use of catalysts offers a wide range of softness, densities, and porosities.
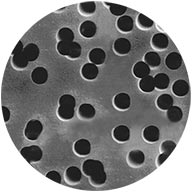
Membranes
Variety of porous membrane solutions that use controlled processes to ensure consistent and repeatable pore structures, including sintered PTFE, Oxyphen track-etched, and PES membranes.

Talk with a Material Science Expert
How Is Porous Plastic Used?
At Porex, our collaborative engineering approach cultivates innovative solutions for both novel and established products. We address functional design complexities in absorption, application, diffusion, filtration, venting, and wicking by leveraging our comprehensive expertise in porous material science, product design, and custom plastic manufacturing.

Absorption Media
Plastic polymers are transformed into porous foam and fiber solutions, pivotal for fluid and contaminant control via absorption. Notably, medical foam derived from porous plastics excels in wound care by efficiently managing fluids and supporting healing.

Applicator Material
Porous solutions enable precise fluid application. For example, porous plastic is used for soft applicators in cosmetics and drug delivery, as well as writing instruments like markers, providing independent liquid control for effective surface coverage.

Diffusion Material
Porous solutions ensure the even spread of liquid, gas, or light. For instance, reed diffuser wicks steadily release fragrance into rooms, serving purposes like home fragrance products, bioprocessing spargers, and semiconductor processing tubes.
Filtration Media
Filtration plays a key role in porous polymer solutions, separating substances in applications like water filters, fuel separation, and medical filtration for inhalers, injectables, and hemodialysis. Porous plastic allows the passage of liquid, gas, light, or sound for material removal. For example, an inhalation device filter ensures clean medicine and reusability.

Venting Media
Porous plastic vents enhance product performance and longevity. For instance, car headlights incorporate automotive lighting protection vents, reducing humidity and enhancing brightness. Venting ensures effective air circulation in various devices, utilizing membranes and plugs to relieve pressure, prevent leaks, enable cooling, and safeguard against the entry of liquids, dust, microbes, and contaminants.
Wicking Media
Porous plastic facilitates liquid transfer through capillary action. Pregnancy test wicks, for example, deliver controlled liquid to result-providing test strips. Wicking utilizes capillary action forces to manage fluid within narrow, porous spaces, independently of or even in opposition to external forces like gravity, like in markers, inkjet printers, and lateral flow assays.
Explore Porous Plastic Solutions for Your Product
If your product involves fluid or gas movement, Porex’s porous plastic solutions can provide significant benefits. If you’re considering a porous plastic component, our material science experts are ready to assist. Reach out to ask an engineer or request a sample, ensuring a customized solution for your unique requirements.
